This course introduces the fundamental concepts, architecture, and applications of expert systems — computer programs that emulate the decision-making ability of human experts. Students will learn about knowledge representation, inference mechanisms, and reasoning under uncertainty. The course covers rule-based systems, knowledge engineering, and the development of expert system shells. Practical examples and case studies illustrate how expert systems are applied in domains such as medicine, finance, and engineering. By the end of the course, students will be able to design, implement, and evaluate simple expert systems using appropriate tools and methodologies.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Knowledge Representation, Inference Engine, Rule-Based Systems, Decision Support.
- Enseignant: Amina Guidoum (Enseignante)
Specific Course Information for Expert Systems
Course Title: Expert Systems
Level: 4th Year (Computer Science)
Weekly Duration: 1 hour and 30 minutes
Coefficient: 2
Course Type: Annual
Course Objectives
The primary goal of this course is to introduce students to expert systems, a key technique in artificial intelligence. Students will gain knowledge about the architecture, inference mechanisms, and the tools and methodologies used in designing and implementing expert systems.
Prerequisites or co-requisites: Artificial Intelligence
Course Content
Module I: Expert Systems
Unit 1: Expert System Introduction
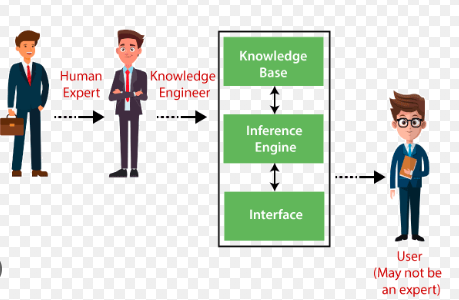
Unit 2. Expert System Architecture
Unit 3: Inference Engine Strategies
Module II: Methodology and Tools for Building an Expert System
Unit 4: Expert Systems Classification
Unit 5: Methodologies
Unit 6: Tools for Building an Expert System
Practical Lab:
- Build a simple Expert System
Final Project:
- Full system analysis and design using selected methodology and tool
Course Outcomes
By the end of this course, students will:
- Understand the foundational concepts of expert systems.
- Be able to explain the architecture and functioning of an inference engine.
- Learn the classification and methodologies involved in creating expert systems.
- Be familiar with the tools available for developing expert systems.
References
- Filippo Peverelli et al., "L’intelligence Artificielle," EIVD Report, Lausanne, 2002.
- F.Y. Villemin, "Intelligence Artificielle B: Introduction et définition," 2001.
- J.-M Karkan & G. Tjoem, "Systèmes Experts: Un nouvel outil pour l’aide à la décision," Edition Masson, 1993.
- R. Voyer, "Moteurs de Systèmes Experts," Edition Eyrolles, 1987.
- H. Farreny & M. Ghallab, "Éléments d’intelligence artificielle," Edition Hermes, 1992.
- François Denis, "Cours d’Intelligence Artificielle: Systèmes Experts."

- Enseignant: Keltoum Benlaharche (Enseignante)